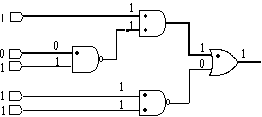
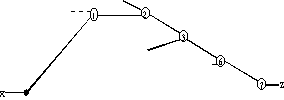
 Figure 1. Example of CPT in a fanout-free circuit
Figure 1. Example of CPT in a fanout-free circuit
Electrical and Computer Engineering Department
Tel: +98-21-800-8485; Fax: +98-21-688690
Massoud Shadfar, Armita Paymandoust, and Zainalabedin Navabi
Faculty of Engineering, Campus No. 2
University of Tehran
14399, Tehran IRAN
Email: navabi_z@irearn.bitnet
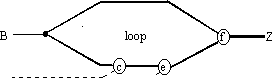
 Figure 1. Example of CPT in a fanout-free circuit
Figure 1. Example of CPT in a fanout-free circuit
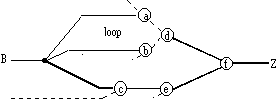
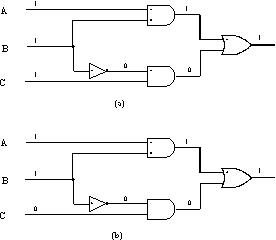 Figure 2. Critical path tracing, with re-convergent fanout
Figure 2. Critical path tracing, with re-convergent fanout
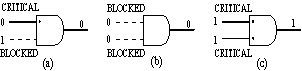

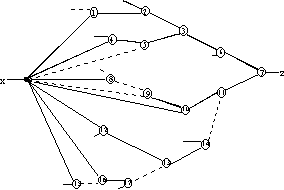
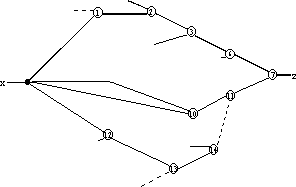
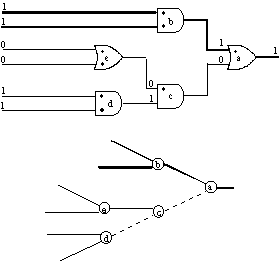 Figure 5. Critical path graph
Figure 5. Critical path graph
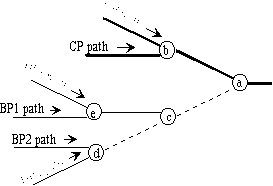 Figure 6. Path kinds
Figure 6. Path kinds
 Figure 7. Rule a replaces two converging critical paths
Figure 7. Rule a replaces two converging critical paths
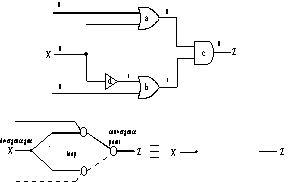 Figure 8. Rule b removes a converging CP and BP
Figure 8. Rule b removes a converging CP and BP
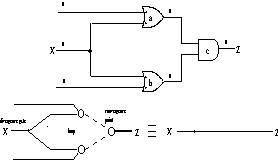 Figure 9. Rule c replaces two converging Bps with a CP
Figure 9. Rule c replaces two converging Bps with a CP
 (a)
(a)
 (a)
(a)

 (a)
(a)
TYPE fsim IS RECORD logic : imp; path_info : bkt; END RECORD; |
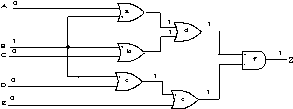
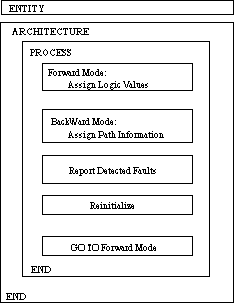 Figure 14. General CPT model structure
Figure 14. General CPT model structure
............ WAIT UNTIL i1.logic /= 'U' AND i2.logic /= 'U'; in1 := i1.logic; in2 := i2.logic; out1 := in1 NAND in2; o.logic <= out1; .............. |
............ --- initialization i1 <= none_U; i2 <= none_U; o <= none_U; --- wait until all lines in circuit initialized. WAIT FOR 10 PS; tn := tn + 1; ........ |
......... ELSIF temp_o(1,1) > -1 THEN IF in1 = '0' AND in2 = '1' THEN temp_i1 := added_node(temp_o,id); temp_i2 := increment_depth(temp_o,id); ELSIF in1 = '1' AND in2 = '0' THEN temp_i1 := increment_depth(temp_o,id); temp_i2 := added_node(temp_o,id); ELSIF in1 = '0' AND in2 = '0' THEN temp_i1 := increment_depth(temp_o,id); temp_i2 := temp_i1; ELSE .......... |
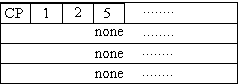 Figure 18. A path information example
Figure 18. A path information example
IF temp_o(1,1) = -1 THEN IF in1 = '1' AND in2 = '0' THEN temp_i1 := uncp; temp_i2 := temp_o; ELSIF in1 = '0' AND in2 = '1' THEN temp_i1 := temp_o; temp_i2 := uncp; ELSIF in1 = '0' AND in2 = '0' THEN temp_i1 := uncp; temp_i2 := uncp; ELSE temp_i1 := temp_o; temp_i2 := temp_o; END IF; |
s. This happens because value of '01' on inputs of an AND gate makes the '0' input critical.
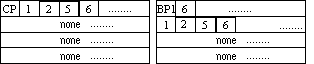
The lower input of gate 2 is being blocked by the upper input. Therefore, the path information on this gate includes the critical path of its output plus an indication that this path is being blocked once at gate 2. Since the lower input of gate 6 is on a critical path with respect to its own output, therefore, the path_info on this input consists of the path information on the output with gate 6 id appended to its first row. On the other hand, since the lower input of gate 7 is being blocked, blockage level is increased by 1 (changing BP1 to BP2) and the blockage information on the output of this gate is copied to the second row of the input path information.
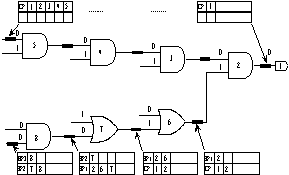 Figure 21. Path information for a simple AND-OR circuit
Figure 21. Path information for a simple AND-OR circuit
FUNCTION backtracing (paths : int_4by20_vector) RETURN int_4by20 IS VARIABLE temp1, temp2 : int_4by20_vector(paths'RANGE); VARIABLE depth, util1 : INTEGER := 0; VARIABLE util2, connection : BOOLEAN := false; VARIABLE num : INTEGER := INTEGER'HIGH; VARIABLE rejector : int_4by20 := rjct; VARIABLE constructed, agent : int_4by20 := none; VARIABLE select1, select2 : INTEGER := -1; |
FOR i IN paths'RANGE LOOP -------- deepest path will be found. IF depth < temp1(i)(1,1) THEN depth := temp1(i)(1,1); END IF; END LOOP; |
......................
IF depth > 0 THEN ------------- construct and reject
FOR i IN depth DOWNTO 1 LOOP
-- path with i depth will be constructed.
FOR j IN paths'RANGE LOOP
IF temp1(j)(1,1) = i THEN
FOR l IN j + 1 TO (paths'LENGTH - 1) LOOP
IF temp1(l)(1,1) = i THEN
replace_check (
temp1(j), temp1(l), constructed, connection);
IF connection THEN
temp1(j) := constructed;
temp1(l) := none;
END IF;
END IF;
END LOOP;
END IF;
END LOOP;
FOR j IN paths'RANGE LOOP
---- path with i-1 depth is rejected
IF temp1(j)(1,1) = i THEN -- by path with i depth.
FOR l IN paths'RANGE LOOP
IF temp1(l)(1,1) = (i - 1) THEN
remove_check (
temp1(j), temp1(l), constructed, connection);
IF connection THEN
temp1(l) := constructed;
END IF;
END IF;
END LOOP;
END IF;
END LOOP;
END LOOP;
END IF;
........
|
...... PI3 : pi GENERIC MAP(3) PORT MAP(S(3)); PI4 : pi GENERIC MAP(4) PORT MAP(S(4)); G8 : or2 GENERIC MAP(9) PORT MAP(S(6),S(4),S(7)); G9 : or2 GENERIC MAP(10) PORT MAP(S(9),S(8),S(10)); G10 : not1 GENERIC MAP(11) PORT MAP(S(10),S(11)); ...... |
TEST:GATE(ID) *****DETECTED SSF***** ] ...... .............................. 1:OR2 ( 9) [I1:sa_0; I2:none; O1:sa_0 ] 1:OR2 (10) [I1:none; I2:none; O1:sa_0 ] 1:NOT (11) [I :sa_0; O :sa_1 ] 1: PO (12) [PO:sa_1; ] 2: PI ( 1) [PI:sa_1; ] 2: PI ( 4) [PI:sa_1; ] ........................................ |